Year 6 Maths NSW Curriculum Topics
Year 6 Maths in NSW is a key transition year that bridges primary maths to the more advanced concepts of high school. Students strengthen core computation skills while building confidence in fractions, decimals, percentages, geometry, data and probability.
Year 6 Maths Topics (Term-by-Term)
Term 1
Fractions • Decimals
Fractions (Operations)
- Addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of fractions
- Understanding equivalence and simplifying where needed
Fractions ↔ Decimals
- Converting between fractions and decimals
- Recognising common equivalents (e.g., 1/4 = 0.25)
Term 2
Decimals • Percentages • Financial Maths
Operations with Decimals
- Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals
- Real-life applications (money, measurement, shopping)
Introduction to Percentages
- Percent means “out of 100”
- Finding a percentage of an amount
Financial Mathematics
- Profit, loss, and simple budgeting scenarios
- Everyday money decisions and estimation
Term 3
2D/3D Geometry • Measurement
2D & 3D Shapes + Angle Properties
- Geometry of 2D and 3D shapes
- Angle properties and recognising key features
Classifying Triangles and Quadrilaterals
- Triangles: scalene, isosceles, equilateral
- Quadrilaterals: square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelogram, trapezium
Circle Features + Measurement
- Radius, diameter, circumference, and area
- Applying formulas to real-life problems
Area, Surface Area & Volume
- Calculating area for common shapes
- Surface area and volume for prisms and composite shapes
Term 4
Cartesian Plane • Negative Numbers • Data • Probability
Cartesian Plane (4 Quadrants)
- Plotting points in all four quadrants
- Understanding coordinate pairs (x, y)
Negative Numbers
- Negative numbers in context (temperature, money, height)
- Computations involving negatives
Data Analysis
- Mean, median, mode
- Interpreting data to make conclusions
Probability of Events
- Probability terms (certain, likely, impossible)
- Expressing probability using fractions
Introduction to Year 6 NSW Curriculum for Maths
The Year 6 Maths NSW curriculum bridges primary school mathematics and secondary learning. Students strengthen computation skills and develop problem-solving, logical reasoning, and real-life application abilities. Year 6 builds confidence, resilience, and a positive attitude toward challenges—setting students up for a smoother transition into Year 7.
Term-by-Term Learning Focus
Term 1: Mastering Fractions
Students develop strong foundations in fraction operations and improve fluency by converting between fractions and decimals. Parents can support learning with visuals (fraction strips, pie charts) and real-life examples (pizza slices, recipes).Term 2: Decimals, Percentages & Money Skills
Students practise decimal operations and learn early financial maths (profit/loss, budgeting). Percentages are introduced as “out of 100”, helping students connect fractions, decimals, and percentages through practical examples like discounts and scores.Term 3: Geometry & Measurement
Students classify shapes, explore circles, and apply measurement formulas to find area, surface area, and volume. These skills build spatial awareness and problem-solving that supports high school topics like trigonometry and algebraic modelling.Term 4: Coordinates, Data & Probability
Students begin graphing by plotting points on the Cartesian plane and applying negative numbers. They also interpret data using mean, median, and mode, and explore probability using fractions and everyday games (dice, spinners, cards).Related Resources
Internal (Aussie Math Tutor NSW)
Trusted External (Authority Links)
Conclusion: The Importance of Year 6 Maths
Year 6 maths is a turning point in a child’s education. From fractions, decimals, and percentages to geometry, data, and probability, this year sets the stage for high school success. With consistent practice and support, students can build strong skills and a positive attitude toward maths. Parents who stay involved can reduce stress and build confidence. A strong Year 6 foundation helps students approach Year 7 with curiosity, resilience, and readiness.Year 6 Maths NSW Curriculum Topics
Year 6 Maths in NSW is a key transition year that bridges primary maths to the more advanced concepts of high school. Students strengthen core computation skills while building confidence in fractions, decimals, percentages, geometry, data and probability.
Year 6 Maths Topics (Term-by-Term)
Term 1
Fractions • Decimals
Fractions (Operations)
- Addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of fractions
- Understanding equivalence and simplifying where needed
Internal: Basics of Fractions ·
Add & Subtract Fractions ·
Multiply & Divide Fractions
External: Khan Academy (Fraction Arithmetic)
Fractions ↔ Decimals
- Converting between fractions and decimals
- Recognising common equivalents (e.g., 1/4 = 0.25)
Internal: Convert Fractions to Decimals
External: MathsIsFun (Fractions & Decimals)
Term 2
Decimals • Percentages • Financial Maths
Operations with Decimals
- Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals
- Real-life applications (money, measurement, shopping)
External: Khan Academy (Decimals)
Introduction to Percentages
- Percent means “out of 100”
- Finding a percentage of an amount
Internal: Percentages Made Easy
External: Khan Academy (Percentages)
Financial Mathematics
- Profit, loss, and simple budgeting scenarios
- Everyday money decisions and estimation
Internal: Simple Interest Guide
Term 3
2D/3D Geometry • Measurement
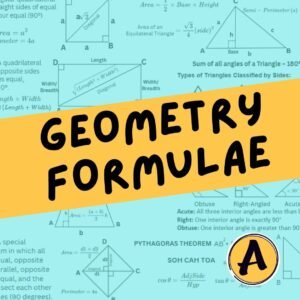
2D & 3D Shapes + Angle Properties
- Geometry of 2D and 3D shapes
- Angle properties and recognising key features
Internal: Triangles, Quadrilaterals & Circles ·
Essential Geometry Formulae
External: MathsIsFun (Geometry)
Classifying Triangles and Quadrilaterals
- Triangles: scalene, isosceles, equilateral
- Quadrilaterals: square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelogram, trapezium
Internal: Triangles & Quadrilaterals Guide
Circle Features + Measurement
- Radius, diameter, circumference, and area
- Applying formulas to real-life problems
Internal: Geometry Formulae (Circles)
External: MathsIsFun (Circles)
Area, Surface Area & Volume
- Calculating area for common shapes
- Surface area and volume for prisms and composite shapes
External: MathsIsFun (Volume)
Term 4
Cartesian Plane • Negative Numbers • Data • Probability
Cartesian Plane (4 Quadrants)
- Plotting points in all four quadrants
- Understanding coordinate pairs (x, y)
Internal: Number Plane – Complete Guide ·
Number Line Maths Game
External: Khan Academy (Coordinate Plane)
Negative Numbers
- Negative numbers in context (temperature, money, height)
- Computations involving negatives
External: MathsIsFun (Negative Numbers)
Data Analysis
- Mean, median, mode
- Interpreting data to make conclusions
External: Math Planet (Statistics)
Probability of Events
- Probability terms (certain, likely, impossible)
- Expressing probability using fractions
Internal: Probability Guide
External: MathsIsFun (Probability)
Introduction to Year 6 NSW Curriculum for Maths
The Year 6 Maths NSW curriculum bridges primary school mathematics and secondary learning. Students strengthen computation skills and develop problem-solving, logical reasoning, and real-life application abilities. Year 6 builds confidence, resilience, and a positive attitude toward challenges—setting students up for a smoother transition into Year 7.
Term-by-Term Learning Focus
Term 1: Mastering Fractions
Students develop strong foundations in fraction operations and improve fluency by converting between fractions and decimals. Parents can support learning with visuals (fraction strips, pie charts) and real-life examples (pizza slices, recipes).
Term 2: Decimals, Percentages & Money Skills
Students practise decimal operations and learn early financial maths (profit/loss, budgeting). Percentages are introduced as “out of 100”, helping students connect fractions, decimals, and percentages through practical examples like discounts and scores.
Term 3: Geometry & Measurement
Students classify shapes, explore circles, and apply measurement formulas to find area, surface area, and volume. These skills build spatial awareness and problem-solving that supports high school topics like trigonometry and algebraic modelling.
Term 4: Coordinates, Data & Probability
Students begin graphing by plotting points on the Cartesian plane and applying negative numbers. They also interpret data using mean, median, and mode, and explore probability using fractions and everyday games (dice, spinners, cards).
Related Resources
Internal (Aussie Math Tutor NSW)
Trusted External (Authority Links)
Conclusion: The Importance of Year 6 Maths
Year 6 maths is a turning point in a child’s education. From fractions, decimals, and percentages to geometry, data, and probability, this year sets the stage for high school success. With consistent practice and support, students can build strong skills and a positive attitude toward maths.
Parents who stay involved can reduce stress and build confidence. A strong Year 6 foundation helps students approach Year 7 with curiosity, resilience, and readiness.