📐 Pythagoras Theorem – Find the Hypotenuse
🧮 Pythagoras – Find the Missing Side
🏠 Pythagoras – Real Life Word Problems
Triangles, Quadrilaterals & Circles Made Crystal-Clear
Geometry helps us understand the shapes we see every day — from tiles on the floor to wheels on a car. In this article, we will classify and describe triangles, quadrilaterals, and circles using their side lengths, angles, and key properties in a clear and easy way.
Understanding Triangles
A triangle is a closed shape made using three straight sides. It has three angles, and the most important rule to remember is:
The sum of all interior angles of a triangle is always 180°.
Triangles are classified in two main ways: by their sides and by their angles.
Types of Triangles Based on Side Lengths
Equilateral Triangle
All three sides are equal in length
All three angles are equal
Each angle measures 60°
Isosceles Triangle
Two sides are equal
The angles opposite the equal sides are also equal
Scalene Triangle
All sides are of different lengths
All angles are different
Types of Triangles Based on Angles
Acute Triangle
All angles are less than 90°
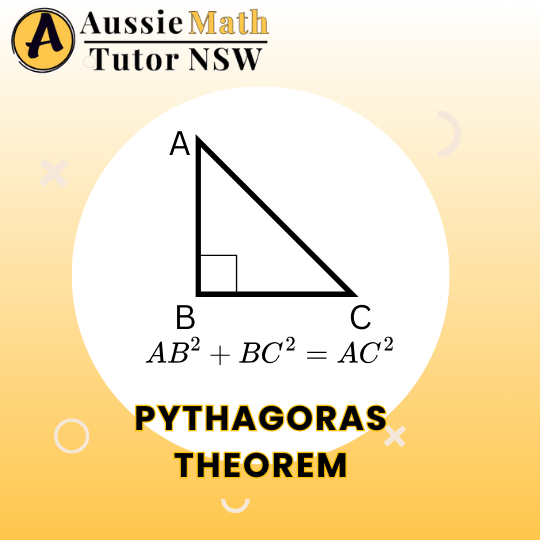
Right-Angled Triangle
One angle is exactly 90°
The longest side (opposite the right angle) is called the hypotenuse
Obtuse Triangle
One angle is greater than 90°
Understanding Quadrilaterals
A quadrilateral is a shape with four sides and four angles.
The total sum of all interior angles in any quadrilateral is:
360°
Quadrilaterals are classified based on side lengths, angle sizes, and parallel sides.
Common Types of Quadrilaterals
Square
All four sides are equal
All angles are 90°
Diagonals are equal and intersect at right angles
Rectangle
Opposite sides are equal
All angles are 90°
Diagonals are equal but do not intersect at right angles
Parallelogram
Opposite sides are equal and parallel
Opposite angles are equal
Adjacent angles add up to 180°
Rhombus
All sides are equal
Opposite sides are parallel
Diagonals intersect at right angles
Trapezium
Only one pair of opposite sides is parallel
The non-parallel sides are not equal in general
Understanding Circles
A circle is a round shape made of all points that are the same distance from a fixed point called the centre. Unlike polygons, a circle has no straight sides and no corners.
Key Parts of a Circle
Radius – distance from the centre to the edge
Diameter – distance across the circle through the centre
Diameter = 2 × Radius
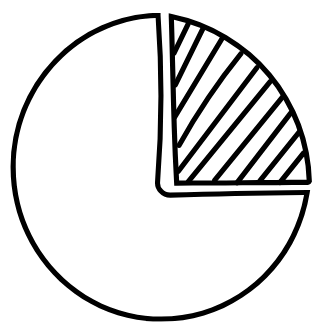
Circumference – distance around the circle
Chord – a line joining two points on the circle
Arc – a curved part of the circumference
Sector – a region formed by two radii and an arc
Important Circle Relationships
The diameter is always the longest chord in a circle
Angles at the centre are twice the size of angles at the circumference standing on the same arc
A radius drawn to the midpoint of a chord meets the chord at right angles
Why Learning Shape Properties Is Important
Understanding the properties of triangles, quadrilaterals, and circles helps students:
Identify shapes quickly in exams
Solve geometry problems with confidence
Build strong foundations for algebra and trigonometry
Apply maths to real-life situations
Final Thoughts
Geometry becomes much easier when shapes are classified logically rather than memorised randomly. By understanding side lengths, angles, and special properties, students can approach geometry questions calmly and accurately.
Practising with diagrams and real examples is the key to mastering this topic.
Struggling with Pythagoras’ Theorem? You’re Not Alone!
If you’re in Year 7, Year 8, or Year 9 maths, chances are you’ve already heard the words “Pythagoras’ Theorem.”
For many students, this topic can feel confusing at first.
Common problems students face include:
“I don’t know when to use the formula.”
“I mix up which side is which.”
“I forget what the hypotenuse is.”
“I don’t understand word problems.”
“I don’t know how to find a missing side.”
The good news?
Once you understand a few key ideas, Pythagoras’ Theorem becomes one of the easiest and most useful maths topics!
Let’s break it down step-by-step in a way that actually makes sense.
What is the Pythagoras Theorem?

According to the Pythagoras Theorem, The Square on the hypotenuse IS EQUAL TO The Sum of the squares on the other two sides.
What are the most important Pythagorean triples every student in Sydney, NSW, should know for the math exam?
Check the common Pythagoras Triplets which will be useful to students in Sydney, NSW. Generally, most of the questions on Pythagoras Theorem will be based on the following numbers also known as Pythagoras Triplets.
(3, 4, 5)
(5, 12, 13)
(6, 8, 10)
(7, 24, 25)
(8, 15, 17)
(9, 12, 15)
(9, 40, 41)
(11, 60, 61)
(12, 35, 37)
(13, 84, 85)
Why is the Pythagorean Theorem important?
The Pythagorean theorem is one of the most important and popular geometry theorems and has a wide range of applications in numerous fields.
Here’s why it’s important:
1. Whenever you see a right-angled triangle, there is a strong possibility that the Pythagorean theorem will be applied, as it makes it easier to find an unknown side of the triangle.
2. The Pythagorean theorem has applications in the fields of geometry, navigation, engineering, physics, trigonometry, and architecture.
Essentially, the Pythagorean theorem provides a fundamental framework for understanding spatial relationships and making calculations in a two-dimensional world.
The Biggest Mistake Students Make
The number one problem students face is:
👉 Not identifying the hypotenuse correctly
Remember this:
The Hypotenuse is ALWAYS:
The longest side
Opposite the right angle
If you get that part right, the rest becomes much easier.
When Do We Use Pythagoras’ Theorem?
You can ONLY use Pythagoras’ Theorem when:
✔ The triangle is a right-angled triangle
✔ You know the length of two sides
✔ You need to find the third side
If the triangle does NOT have a right angle, Pythagoras cannot be used.
Where Is Pythagoras Used in Real Life?
Pythagoras’ Theorem is not just a school topic.
It is used in:
Architecture and construction
Building ramps and roofs
Navigation and GPS
Engineering
Video game graphics
Physics and technology
Understanding this theorem helps build strong problem-solving skills for many future subjects.
Practice Makes Perfect
The only real way to get confident with Pythagoras is:
✔ Doing lots of practice
✔ Solving different types of questions
✔ Understanding word problems
✔ Learning to identify right-angled triangles quickly
Need Extra Help with Pythagoras?
If your child is finding Pythagoras’ Theorem confusing, personalised tutoring can make a huge difference.
At Aussie Math Tutor NSW, we help students:
Understand Pythagoras step-by-step
Improve confidence in geometry
Solve exam-style questions
Prepare for tests and NAPLAN
Master problem-solving skills
Pythagorean Theorem Easy Practice Test
Pythagoras Theorem Applications
Ever wonder how builders ensure walls are square or how sailors navigate using distances? That’s the power of Pythagoras’ Theorem in action! For Sydney and NSW students, tackling word problems isn’t just about numbers; it’s about unlocking this real-world magic. These puzzles sharpen your detective skills, making you spot hidden right triangles and use the famous Pythagoras Theorem to solve mysteries of length and distance.