Understanding the basic geometry formulae for common two-dimensional shapes is essential for a variety of mathematical and practical applications. This section will cover the key formulae for calculating the area, perimeter, and other relevant measurements for triangles, squares, rectangles, parallelograms, and circles.

Formulae for Circles
Circles, which are fundamentally different due to their curved nature, require specific formulae:
Area = π x radius x radius
Circumference = 2 x π x radius
Additionally, the relationship between the radius and diameter is:
Diameter = 2 x radius

Formulae for Triangles
For triangles, the most fundamental formula for calculating the area is:
Area = (1/2) x base x height
Additionally, Heron’s formula, which is useful when the lengths of all three sides are known, is given by:
Area = √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)]
where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle, calculated as:
s = (a + b + c) / 2

Formulae for Square
For squares, the formulae are straightforward:
Area = side x side
Perimeter = 4 x side

Formulae for Rectangle
Rectangles share similar simplicity in their calculations:
Area = length x width
Perimeter = 2 x (length + width)
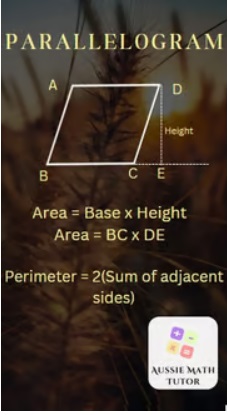
Formulae For Parallelogram
Parallelograms, which are often confused with rectangles, have their own set of formulae:
Area = base x height
Perimeter = 2 x (base + side length)
These formulae serve as the foundation for more complex geometric calculations and are used extensively in various fields such as engineering, architecture, and physics. By mastering these basic geometry formulae, one can efficiently solve a wide range of practical and theoretical problems.